Memory usage#
Links: notebook, html, PDF, python, slides, GitHub
The first benchmark based on scikti-learn’s benchmark shows high peaks of memory usage for the python runtime on linear models. Let’s see how to measure that.
from jyquickhelper import add_notebook_menu
add_notebook_menu()
Artificial huge data#
import numpy
N, nfeat = 300000, 200
N * nfeat * 8 / 1e9
0.48
X = numpy.random.random((N, nfeat))
y = numpy.empty((N, 50))
for i in range(y.shape[1]):
y[:, i] = X.sum(axis=1) + numpy.random.random(N)
X.shape, y.shape
((300000, 200), (300000, 50))
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, train_size=0.1)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
clr = LinearRegression()
clr.fit(X_train, y_train)
LinearRegression()
from mlprodict.onnx_conv import to_onnx
from mlprodict.onnxrt import OnnxInference
clr_onnx = to_onnx(clr, X_train[:1].astype(numpy.float32))
oinfpy = OnnxInference(clr_onnx, runtime='python')
Let’s minimize the cost of verifications on scikit-learn’s side.
from sklearn import set_config
set_config(assume_finite=True)
Profiling the prediction function#
from pyquickhelper.pycode.profiling import profile
print(profile(lambda: clr.predict(X_test),
pyinst_format='text')[1])
_ ._ __/__ _ _ _ _ _/_ Recorded: 15:51:37 Samples: 4 /_//_/// /_/ //_// / //_'/ // Duration: 0.439 CPU time: 0.797 / _/ v3.0.1 Program: c:python372_x64libsite-packagesipykernel_launcher.py -f C:UsersxavieAppDataRoamingjupyterruntimekernel-4e37b7b5-7bfc-4784-9e5a-cae5acd320c1.json 0.439 profile pyquickhelperpycodeprofiling.py:49 |- 0.427 <lambda> <ipython-input-12-1097e70fe6c7>:2 | `- 0.427 predict sklearnlinear_model_base.py:222 | `- 0.427 _decision_function sklearnlinear_model_base.py:215 | |- 0.371 inner_f sklearnutilsvalidation.py:60 | | `- 0.370 safe_sparse_dot sklearnutilsextmath.py:118 | `- 0.056 [self] `- 0.012 [self]
import numpy
def nastype32(mat):
return mat.astype(numpy.float32)
print(profile(lambda: oinfpy.run({'X': nastype32(X_test)}),
pyinst_format='text')[1])
_ ._ __/__ _ _ _ _ _/_ Recorded: 15:51:39 Samples: 5 /_//_/// /_/ //_// / //_'/ // Duration: 0.378 CPU time: 0.453 / _/ v3.0.1 Program: c:python372_x64libsite-packagesipykernel_launcher.py -f C:UsersxavieAppDataRoamingjupyterruntimekernel-4e37b7b5-7bfc-4784-9e5a-cae5acd320c1.json 0.378 profile pyquickhelperpycodeprofiling.py:49 |- 0.370 <lambda> <ipython-input-13-da4aa05db7ed>:6 | |- 0.233 run mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference.py:471 | | `- 0.233 _run_sequence_runtime mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference.py:551 | | `- 0.233 run mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference_node.py:141 | | `- 0.233 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:374 | | `- 0.233 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:289 | | `- 0.233 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_linear_regressor.py:27 | | |- 0.215 numpy_dot_inplace mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op_numpy_helper.py:8 | | | `- 0.215 dot <__array_function__ internals>:2 | | `- 0.018 [self] | |- 0.112 nastype32 <ipython-input-13-da4aa05db7ed>:3 | `- 0.026 [self] `- 0.008 [self]
Most of the time is taken out into casting into float. Let’s take it out.
X_test32 = X_test.astype(numpy.float32)
print(profile(lambda: oinfpy.run({'X': X_test32}),
pyinst_format='text')[1])
_ ._ __/__ _ _ _ _ _/_ Recorded: 15:51:43 Samples: 3 /_//_/// /_/ //_// / //_'/ // Duration: 0.081 CPU time: 0.141 / _/ v3.0.1 Program: c:python372_x64libsite-packagesipykernel_launcher.py -f C:UsersxavieAppDataRoamingjupyterruntimekernel-4e37b7b5-7bfc-4784-9e5a-cae5acd320c1.json 0.080 profile pyquickhelperpycodeprofiling.py:49 |- 0.074 <lambda> <ipython-input-14-fe055596e921>:3 | `- 0.074 run mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference.py:471 | `- 0.074 _run_sequence_runtime mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference.py:551 | `- 0.074 run mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference_node.py:141 | `- 0.074 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:374 | `- 0.074 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:289 | `- 0.074 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_linear_regressor.py:27 | |- 0.059 numpy_dot_inplace mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op_numpy_helper.py:8 | | `- 0.059 dot <__array_function__ internals>:2 | `- 0.015 [self] `- 0.007 [self]
Much better.
SGDClasifier#
This models is implemented with many ONNX nodes. Let’s how it behaves.
from sklearn.linear_model import SGDClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
data = load_iris()
Xir, yir = data.data, data.target
Xir_train, Xir_test, yir_train, yir_test = train_test_split(Xir, yir)
sgcl = SGDClassifier()
sgcl.fit(Xir_train, yir_train)
SGDClassifier()
sgd_onnx = to_onnx(sgcl, Xir_train.astype(numpy.float32))
C:xavierdupre__home_github_forkscikit-learnsklearnutilsdeprecation.py:101: FutureWarning: Attribute average_coef_ was deprecated in version 0.23 and will be removed in 0.25. warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning) C:xavierdupre__home_github_forkscikit-learnsklearnutilsdeprecation.py:101: FutureWarning: Attribute average_intercept_ was deprecated in version 0.23 and will be removed in 0.25. warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning) C:xavierdupre__home_github_forkscikit-learnsklearnutilsdeprecation.py:101: FutureWarning: Attribute standard_coef_ was deprecated in version 0.23 and will be removed in 0.25. warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning) C:xavierdupre__home_github_forkscikit-learnsklearnutilsdeprecation.py:101: FutureWarning: Attribute standard_intercept_ was deprecated in version 0.23 and will be removed in 0.25. warnings.warn(msg, category=FutureWarning)
%load_ext mlprodict
%onnxview sgd_onnx
sgd_oinf = OnnxInference(sgd_onnx)
def call_n_times_x1(n, X_test, sgd_oinf):
for i in range(n):
res = sgd_oinf.run({'X': X_test})
return res
call_n_times_x1(20, Xir_test[:1].astype(numpy.float32), sgd_oinf)
{'output_label': array([0], dtype=int64),
'output_probability': [{0: -65.8407, 1: -158.60867, 2: -100.55802}]}
sgcl.decision_function(Xir_test[:1])
array([[ -65.840706 , -158.60864916, -100.55799704]])
xir_32 = Xir_test[:1].astype(numpy.float32)
print(profile(lambda: call_n_times_x1(20000, xir_32, sgd_oinf),
pyinst_format='text')[1])
_ ._ __/__ _ _ _ _ _/_ Recorded: 15:52:03 Samples: 1022 /_//_/// /_/ //_// / //_'/ // Duration: 1.432 CPU time: 1.453 / _/ v3.0.1 Program: c:python372_x64libsite-packagesipykernel_launcher.py -f C:UsersxavieAppDataRoamingjupyterruntimekernel-4e37b7b5-7bfc-4784-9e5a-cae5acd320c1.json 1.432 profile pyquickhelperpycodeprofiling.py:49 `- 1.432 <lambda> <ipython-input-22-ec5a6181dc40>:3 `- 1.432 call_n_times_x1 <ipython-input-20-32f502ef162e>:1 |- 1.412 run mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference.py:471 | |- 1.381 _run_sequence_runtime mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference.py:551 | | |- 1.218 run mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference_node.py:141 | | | |- 0.398 [self] | | | |- 0.311 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:132 | | | | |- 0.193 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_array_feature_extractor.py:59 | | | | | |- 0.170 _array_feature_extrator mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_array_feature_extractor.py:17 | | | | | `- 0.023 [self] | | | | |- 0.047 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_cast.py:37 | | | | | `- 0.033 _run_inplace mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_cast.py:42 | | | | | `- 0.020 <lambda> mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_cast.py:35 | | | | |- 0.028 [self] | | | | |- 0.022 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_zipmap.py:221 | | | | `- 0.021 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_reshape.py:16 | | | |- 0.299 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:337 | | | | `- 0.287 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:289 | | | | `- 0.281 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_argmax.py:69 | | | | `- 0.277 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_argmax.py:42 | | | | `- 0.271 _argmax mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_argmax.py:12 | | | | |- 0.159 expand_dims <__array_function__ internals>:2 | | | | | `- 0.155 expand_dims numpylibshape_base.py:512 | | | | | [10 frames hidden] numpy | | | | |- 0.059 argmax <__array_function__ internals>:2 | | | | | |- 0.041 argmax numpycorefromnumeric.py:1112 | | | | | | [4 frames hidden] numpy | | | | | `- 0.018 [self] | | | | `- 0.052 [self] | | | |- 0.171 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:517 | | | | |- 0.155 run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:453 | | | | | |- 0.075 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op.py:550 | | | | | `- 0.067 _run mlprodictonnxrtops_cpuop_matmul.py:16 | | | | | `- 0.066 numpy_dot_inplace mlprodictonnxrtops_cpu_op_numpy_helper.py:8 | | | | | `- 0.055 dot <__array_function__ internals>:2 | | | | `- 0.016 [self] | | | `- 0.038 <genexpr> mlprodictonnxrtonnx_inference_node.py:153 | | `- 0.158 [self] | `- 0.031 [self] `- 0.020 [self]
The code in mlprodict/onnxrt/onnx_inference_node.py just calls an
operator and updates the list containing all the results. The time in
here is significant if the number of node is huge if the python runtime
is used.
Memory profiling#
%matplotlib inline
from memory_profiler import memory_usage
memprof_skl = memory_usage((clr.predict, (X_test, )), timestamps=True, interval=0.01)
memprof_skl
[(811.3515625, 1594129928.0175571),
(811.671875, 1594129932.2684996),
(822.36328125, 1594129932.28645),
(832.11328125, 1594129932.30241),
(847.05078125, 1594129932.3183646),
(860.5625, 1594129932.333325),
(874.48828125, 1594129932.3482847),
(883.73828125, 1594129932.3642418),
(898.80078125, 1594129932.380199),
(907.98828125, 1594129932.3961573),
(935.03515625, 1594129932.4121134),
(965.03515625, 1594129932.4280717),
(998.59765625, 1594129932.4440289),
(949.73828125, 1594129932.4599853),
(914.75390625, 1594129932.464972)]
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pandas import DataFrame, to_datetime
def mem_profile_plot(mem, title):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(4, 4))
df = DataFrame(mem, columns=["memory", "timestamp"])
df["timestamp"] = to_datetime(df.timestamp)
df["timestamp"] -= df.timestamp.min()
df.set_index("timestamp").plot(ax=ax)
ax.set_title(title + "\nmemory usage")
return ax
mem_profile_plot(memprof_skl, "clr.predict");
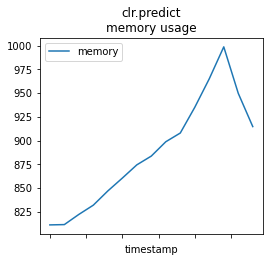
memprof_onx = memory_usage((oinfpy.run, ({'X': X_test32}, )), timestamps=True, interval=0.01)
mem_profile_plot(memprof_onx, "oinfpy.run");
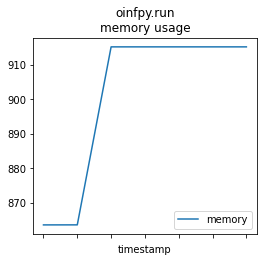
memprof_onx2 = memory_usage((oinfpy.run, ({'X': X_test.astype(numpy.float32, copy=False)}, )),
timestamps=True, interval=0.01)
mem_profile_plot(memprof_onx2, "oinfpy.run + astype(numpy.float32)");
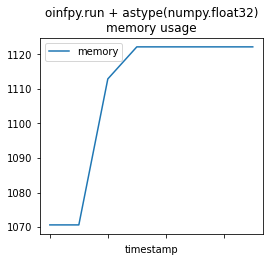
This is not very informative.
Memory profiling outside the notebook#
More precise.
%%writefile mprof_clr_predict.py
import numpy
N, nfeat = 300000, 200
X = numpy.random.random((N, nfeat))
y = numpy.empty((N, 50))
for i in range(y.shape[1]):
y[:, i] = X.sum(axis=1) + numpy.random.random(N)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, train_size=0.1)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
clr = LinearRegression()
clr.fit(X_train, y_train)
from sklearn import set_config
set_config(assume_finite=True)
from memory_profiler import profile
@profile
def clr_predict():
clr.predict(X_test)
clr_predict()
Overwriting mprof_clr_predict.py
!python -m memory_profiler mprof_clr_predict.py --timestamp
Filename: mprof_clr_predict.py
Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
20 1234.7 MiB 1234.7 MiB @profile
21 def clr_predict():
The notebook seems to increase the memory usage.
%%writefile mprof_onnx_run.py
import numpy
N, nfeat = 300000, 200
X = numpy.random.random((N, nfeat))
y = numpy.empty((N, 50))
for i in range(y.shape[1]):
y[:, i] = X.sum(axis=1) + numpy.random.random(N)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, train_size=0.1)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
clr = LinearRegression()
clr.fit(X_train, y_train)
from mlprodict.onnx_conv import to_onnx
from mlprodict.onnxrt import OnnxInference
clr_onnx = to_onnx(clr, X_train[:1].astype(numpy.float32))
oinfpy = OnnxInference(clr_onnx, runtime='python')
X_test32 = X_test.astype(numpy.float32)
from sklearn import set_config
set_config(assume_finite=True)
from memory_profiler import profile
@profile
def oinfpy_predict():
oinfpy.run({'X': X_test32})
oinfpy_predict()
Overwriting mprof_onnx_run.py
!python -m memory_profiler mprof_onnx_run.py --timestamp
Filename: mprof_onnx_run.py
Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
26 1498.8 MiB 1498.8 MiB @profile
27 def oinfpy_predict():
28 1500.1 MiB 1.3 MiB oinfpy.run({'X': X_test32})
%%writefile mprof_onnx_run32.py
import numpy
N, nfeat = 300000, 200
X = numpy.random.random((N, nfeat))
y = numpy.empty((N, 50))
for i in range(y.shape[1]):
y[:, i] = X.sum(axis=1) + numpy.random.random(N)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, train_size=0.1)
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
clr = LinearRegression()
clr.fit(X_train, y_train)
from mlprodict.onnx_conv import to_onnx
from mlprodict.onnxrt import OnnxInference
clr_onnx = to_onnx(clr, X_train[:1].astype(numpy.float32))
oinfpy = OnnxInference(clr_onnx, runtime='python')
from sklearn import set_config
set_config(assume_finite=True)
from memory_profiler import profile
@profile
def oinfpy_predict32():
oinfpy.run({'X': X_test.astype(numpy.float32)})
oinfpy_predict32()
Overwriting mprof_onnx_run32.py
!python -m memory_profiler mprof_onnx_run32.py --timestamp
Filename: mprof_onnx_run32.py
Line # Mem usage Increment Line Contents
================================================
25 1293.1 MiB 1293.1 MiB @profile
26 def oinfpy_predict32():
27 1294.4 MiB 1.3 MiB oinfpy.run({'X': X_test.astype(numpy.float32)})