ONNX FFTs#
Links: notebook, html, PDF, python, slides, GitHub
Implementation of a couple of variations of FFT (see FFT in ONNX.
from jyquickhelper import add_notebook_menu
add_notebook_menu()
%matplotlib inline
%load_ext mlprodict
Signature#
We try to use function FFT or torch.fft.fftn.
import numpy
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
def numpy_fftn(x, fft_type, fft_length, axes):
"""
Implements FFT
:param x: input
:param fft_type: string (see below)
:param fft_length: length on each axis of axes
:param axes: axes
:return: result
* `'FFT`': complex-to-complex FFT. Shape is unchanged.
* `'IFFT`': Inverse complex-to-complex FFT. Shape is unchanged.
* `'RFFT`': Forward real-to-complex FFT.
Shape of the innermost axis is reduced to fft_length[-1] // 2 + 1 if fft_length[-1]
is a non-zero value, omitting the reversed conjugate part of
the transformed signal beyond the Nyquist frequency.
* `'IRFFT`': Inverse real-to-complex FFT (ie takes complex, returns real).
Shape of the innermost axis is expanded to fft_length[-1] if fft_length[-1]
is a non-zero value, inferring the part of the transformed signal beyond the Nyquist
frequency from the reverse conjugate of the 1 to fft_length[-1] // 2 + 1 entries.
"""
if fft_type == 'FFT':
return numpy.fft.fftn(x, fft_length, axes=axes)
raise NotImplementedError("Not implemented for fft_type=%r." % fft_type)
def test_fct(fct1, fct2, fft_type='FFT', decimal=5):
cases = list(range(4, 20))
dims = [[c] for c in cases] + [[4,4,4,4], [4,5,6,7]]
lengths_axes = [([c], [0]) for c in cases] + [
([2, 2, 2, 2], None), ([2, 6, 7, 2], None), ([2, 3, 4, 5], None),
([2], [3]), ([3], [2])]
n_test = 0
for ndim in range(1, 5):
for dim in dims:
for length, axes in lengths_axes:
if axes is None:
axes = range(ndim)
di = dim[:ndim]
axes = [min(len(di) - 1, a) for a in axes]
le = length[:ndim]
if len(length) > len(di):
continue
mat = numpy.random.randn(*di).astype(numpy.float32)
try:
v1 = fct1(mat, fft_type, le, axes=axes)
except Exception as e:
raise AssertionError(
"Unable to run %r mat.shape=%r ndim=%r di=%r fft_type=%r le=%r "
"axes=%r exc=%r" %(
fct1, mat.shape, ndim, di, fft_type, le, axes, e))
v2 = fct2(mat, fft_type, le, axes=axes)
try:
assert_almost_equal(v1, v2, decimal=decimal)
except AssertionError as e:
raise AssertionError(
"Failure mat.shape=%r, fft_type=%r, fft_length=%r" % (
mat.shape, fft_type, le)) from e
n_test += 1
return n_test
test_fct(numpy_fftn, numpy_fftn)
1302
%timeit -n 1 -r 1 test_fct(numpy_fftn, numpy_fftn)
1.81 s ± 0 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 run, 1 loop each)
import torch
def torch_fftn(x, fft_type, fft_length, axes):
xt = torch.tensor(x)
if fft_type == 'FFT':
return torch.fft.fftn(xt, fft_length, axes).cpu().detach().numpy()
%timeit -n 1 -r 1 test_fct(numpy_fftn, torch_fftn)
2.07 s ± 0 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 run, 1 loop each)
Numpy implementation#
import numpy
def _dft_cst(N, fft_length, dtype):
def _arange(dim, dtype, resh):
return numpy.arange(dim).astype(dtype).reshape(resh)
def _prod(n, k):
return (-2j * numpy.pi * k / fft_length) * n
def _exp(m):
return numpy.exp(m)
n = _arange(N, dtype, (-1, 1))
k = _arange(fft_length, dtype, (1, -1))
M = _exp(_prod(n, k))
return M
def custom_fft(x, fft_type, length, axis, dft_fct=None):
# https://github.com/numpy/numpy/blob/4adc87dff15a247e417d50f10cc4def8e1c17a03/numpy/fft/_pocketfft.py#L56
if dft_fct is None:
dft_fct = _dft_cst
if fft_type == 'FFT':
if x.shape[axis] > length:
# fft_length > shape on the same axis
# the matrix is shortened
slices = [slice(None)] * len(x.shape)
slices[axis] = slice(0, length)
new_x = x[tuple(slices)]
elif x.shape[axis] == length:
new_x = x
else:
# other, the matrix is completed with zeros
shape = list(x.shape)
shape[axis] = length
slices = [slice(None)] * len(x.shape)
slices[axis] = slice(0, length)
zeros = numpy.zeros(tuple(shape), dtype=x.dtype)
index = [slice(0, i) for i in x.shape]
zeros[tuple(index)] = x
new_x = zeros
cst = dft_fct(new_x.shape[axis], length, x.dtype)
perm = numpy.arange(len(x.shape)).tolist()
if perm[axis] == perm[-1]:
res = numpy.matmul(new_x, cst).transpose(perm)
else:
perm[axis], perm[-1] = perm[-1], perm[axis]
rest = new_x.transpose(perm)
res = numpy.matmul(rest, cst).transpose(perm)
perm[axis], perm[0] = perm[0], perm[axis]
return res
raise ValueError("Unexpected value for fft_type=%r." % fft_type)
def custom_fftn(x, fft_type, fft_length, axes, dft_fct=None):
if len(axes) != len(fft_length):
raise ValueError("Length mismatch axes=%r, fft_length=%r." % (
axes, fft_length))
if fft_type == 'FFT':
res = x
for i in range(len(fft_length) - 1, -1, -1):
length = fft_length[i]
axis = axes[i]
res = custom_fft(res, fft_type, length, axis, dft_fct=dft_fct)
return res
raise ValueError("Unexpected value for fft_type=%r." % fft_type)
shape = (4, )
fft_length = [5,]
axes = [0]
rnd = numpy.random.randn(*shape) + numpy.random.randn(*shape) * 1j
custom_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes), numpy_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes)
assert_almost_equal(custom_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes),
numpy_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes), decimal=5)
shape = (4, 3)
fft_length = [3, 2]
axes = [0, 1]
rnd = numpy.random.randn(*shape) + numpy.random.randn(*shape) * 1j
custom_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes), numpy_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes)
assert_almost_equal(custom_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes),
numpy_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes), decimal=5)
%timeit -n 1 -r 1 test_fct(numpy_fftn, custom_fftn, decimal=4)
2.35 s ± 0 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 run, 1 loop each)
Benchmark#
from cpyquickhelper.numbers.speed_measure import measure_time
from tqdm import tqdm
from pandas import DataFrame
def benchmark(fcts, power2=False):
axes = [1]
if power2:
shape = [512, 1024]
lengths = [2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024]
else:
shape = [512, 150]
lengths = list(range(8, 200, 8))
rnd = numpy.random.randn(*shape) + numpy.random.randn(*shape) * 1j
data = []
for length in tqdm(lengths):
fft_length = [length]
for name, fct in fcts.items():
obs = measure_time(lambda: fct(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes),
repeat=5, number=5)
obs['name'] = name
obs['length'] = length
data.append(obs)
df = DataFrame(data)
return df
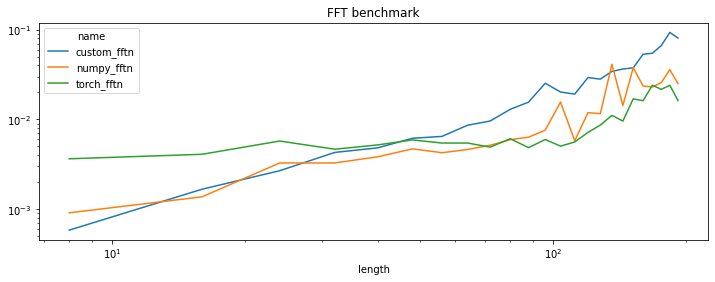
df = benchmark({'numpy_fftn': numpy_fftn, 'custom_fftn': custom_fftn, 'torch_fftn': torch_fftn})
piv = df.pivot("length", "name", "average")
piv[:5]
100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:06<00:00, 3.91it/s]
| name | custom_fftn | numpy_fftn | torch_fftn |
|---|---|---|---|
| length | |||
| 8 | 0.000585 | 0.000911 | 0.003643 |
| 16 | 0.001669 | 0.001373 | 0.004087 |
| 24 | 0.002682 | 0.003273 | 0.005745 |
| 32 | 0.004288 | 0.003275 | 0.004657 |
| 40 | 0.004818 | 0.003831 | 0.005198 |
piv.plot(logy=True, logx=True, title="FFT benchmark", figsize=(12, 4));
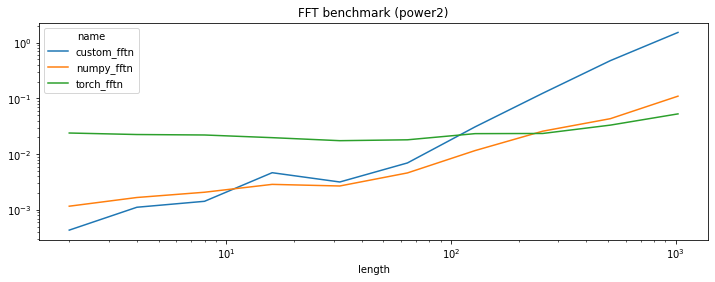
df = benchmark({'numpy_fftn': numpy_fftn, 'custom_fftn': custom_fftn, 'torch_fftn': torch_fftn},
power2=True)
piv = df.pivot("length", "name", "average")
piv
100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:13<00:00, 1.33s/it]
| name | custom_fftn | numpy_fftn | torch_fftn |
|---|---|---|---|
| length | |||
| 2 | 0.000434 | 0.001167 | 0.023980 |
| 4 | 0.001117 | 0.001671 | 0.022530 |
| 8 | 0.001428 | 0.002077 | 0.022102 |
| 16 | 0.004654 | 0.002874 | 0.019792 |
| 32 | 0.003172 | 0.002689 | 0.017474 |
| 64 | 0.006966 | 0.004612 | 0.018116 |
| 128 | 0.030904 | 0.011608 | 0.023369 |
| 256 | 0.123821 | 0.025853 | 0.023532 |
| 512 | 0.476802 | 0.043352 | 0.033228 |
| 1024 | 1.527917 | 0.109868 | 0.052858 |
piv.plot(logy=True, logx=True, title="FFT benchmark (power2)", figsize=(12, 4));
Profiling#
from pyquickhelper.pycode.profiling import profile2graph, profile
shape = [512, 128]
fft_length = [128]
axes = [1]
rnd = numpy.random.randn(*shape) + numpy.random.randn(*shape) * 1j
def f():
for i in range(100):
custom_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes)
stat, text = profile(f)
gr = profile2graph(stat)
print(gr[0].to_text(fct_width=40))
f -- 1 1 -- 0.01752 0.54515 -- <ipython-input-81-3ee1763130c2>:8:f (f)
custom_fftn -- 100 100 -- 0.00234 0.52763 -- <ipython-input-7-85a4c9f552d3>:57:custom_fftn (custom_fftn)
custom_fft -- 100 100 -- 0.19936 0.52516 -- <ipython-input-7-85a4c9f552d3>:20:custom_fft (custom_fft)
_dft_cst -- 100 100 -- 0.31917 0.32366 -- <ipython-input-61-afe90fb073f9>:4:_dft_cst (_dft_cst)
_arange -- 200 200 -- 0.00088 0.00449 -- <ipython-input-61-afe90fb073f9>:5:_arange (_arange)
<method '...objects> -- 200 200 -- 0.00128 0.00128 -- ~:0:<method 'astype' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects> (<method 'astype' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects>)
<method '...objects> -- 200 200 -- 0.00064 0.00064 -- ~:0:<method 'reshape' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects> (<method 'reshape' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects>)
<built-in....arange> -- 200 200 -- 0.00169 0.00169 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.arange> (<built-in method numpy.arange>) +++
<built-in met...uiltins.len> -- 100 100 -- 0.00011 0.00011 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<method 'toli...ay' objects> -- 100 100 -- 0.00024 0.00024 -- ~:0:<method 'tolist' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects> (<method 'tolist' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects>)
<method 'tran...ay' objects> -- 100 100 -- 0.00076 0.00076 -- ~:0:<method 'transpose' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects> (<method 'transpose' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects>)
<built-in met...umpy.arange> -- 100 100 -- 0.00102 0.00102 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.arange> (<built-in method numpy.arange>) +++
<built-in method builtins.len> -- 300 300 -- 0.00013 0.00013 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<built-in method builtins.len> -- 400 400 -- 0.00024 0.00024 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>)
<built-in method numpy.arange> -- 300 300 -- 0.00271 0.00271 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.arange> (<built-in method numpy.arange>)
We can see that function _dft_cst is the bottle neck and more
precisely the exponential. We need to use the symmetries of the matrix
it builds.
Faster _dft_cst#
The function builds the matrix
where
and
. So it computes powers of the unity
roots.
We use that expression to reduce the number of exponentiels to compute.
import numpy
from numpy.testing import assert_almost_equal
def _dft_cst(N, fft_length, dtype=numpy.float32):
def _arange(dim, dtype, resh):
return numpy.arange(dim).astype(dtype).reshape(resh)
n = _arange(N, dtype, (-1, 1))
k = _arange(fft_length, dtype, (1, -1))
M = (-2j * numpy.pi * k / fft_length) * n
numpy.exp(M, out=M)
return M
M = _dft_cst(3, 4, numpy.float32)
M.shape, M.dtype
((3, 4), dtype('complex64'))
M = _dft_cst(4, 3, numpy.float64)
M.shape, M.dtype
((4, 3), dtype('complex128'))
M
array([[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, 1. +0.00000000e+00j, 1. +0.00000000e+00j],
[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, -0.5-8.66025404e-01j, -0.5+8.66025404e-01j],
[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, -0.5+8.66025404e-01j, -0.5-8.66025404e-01j],
[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, 1. +2.44929360e-16j, 1. +4.89858720e-16j]])
def _dft_cst_power(N, fft_length, dtype=numpy.float32):
if dtype == numpy.float32:
ctype = numpy.complex64
else:
ctype = numpy.complex128
M = numpy.empty((N, fft_length), dtype=ctype)
M[0, :] = 1
M[1, 0] = 1
root = numpy.exp(numpy.pi / fft_length * (-2j))
current = root
M[1, 1] = root
for i in range(2, M.shape[1]):
current *= root
M[1, i] = current
for i in range(2, M.shape[0]):
numpy.multiply(M[i-1, :], M[1, :], out=M[i, :])
return M
M_pow = _dft_cst_power(4, 3, numpy.float64)
M_pow
array([[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, 1. +0.00000000e+00j, 1. +0.00000000e+00j],
[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, -0.5-8.66025404e-01j, -0.5+8.66025404e-01j],
[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, -0.5+8.66025404e-01j, -0.5-8.66025404e-01j],
[ 1. +0.00000000e+00j, 1. +6.10622664e-16j, 1. +1.22124533e-15j]])
assert_almost_equal(M, M_pow)
dims = (10, 15)
assert_almost_equal(_dft_cst(*dims, dtype=numpy.float32),
_dft_cst_power(*dims, dtype=numpy.float32),
decimal=5)
Benchmark again#
def custom_fftn_power(*args, **kwargs):
return custom_fftn(*args, dft_fct=_dft_cst_power, **kwargs)
%timeit -r 1 -n 1 test_fct(numpy_fftn, custom_fftn_power, decimal=4)
1.46 s ± 0 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 run, 1 loop each)
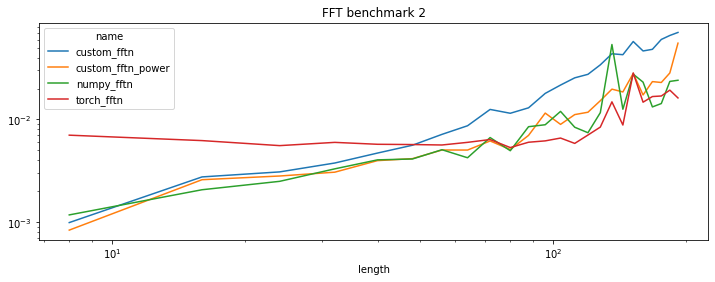
df = benchmark({
'numpy_fftn': numpy_fftn, 'torch_fftn': torch_fftn, 'custom_fftn': custom_fftn,
'custom_fftn_power': custom_fftn_power})
piv = df.pivot("length", "name", "average")
piv[:5]
100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:07<00:00, 3.19it/s]
| name | custom_fftn | custom_fftn_power | numpy_fftn | torch_fftn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| length | ||||
| 8 | 0.000991 | 0.000837 | 0.001177 | 0.007033 |
| 16 | 0.002758 | 0.002591 | 0.002069 | 0.006228 |
| 24 | 0.003087 | 0.002816 | 0.002499 | 0.005564 |
| 32 | 0.003767 | 0.003068 | 0.003306 | 0.005985 |
| 40 | 0.004710 | 0.003975 | 0.004044 | 0.005733 |
piv.plot(logy=True, logx=True, title="FFT benchmark 2", figsize=(12, 4));
from pyquickhelper.pycode.profiling import profile2graph, profile
shape = [512, 128]
fft_length = [128]
axes = [1]
rnd = numpy.random.randn(*shape) + numpy.random.randn(*shape) * 1j
def f():
for i in range(100):
custom_fftn_power(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes)
stat, text = profile(f)
gr = profile2graph(stat)
print(gr[0].to_text(fct_width=40))
f -- 1 1 -- 0.02624 0.57688 -- <ipython-input-92-112d00957d81>:8:f (f)
custom_fftn_power -- 100 100 -- 0.00094 0.55064 -- <ipython-input-88-b403af8c0b43>:1:custom_fftn_power (custom_fftn_power)
custom_fftn -- 100 100 -- 0.00609 0.54970 -- <ipython-input-7-85a4c9f552d3>:57:custom_fftn (custom_fftn)
custom_fft -- 100 100 -- 0.46378 0.54342 -- <ipython-input-7-85a4c9f552d3>:20:custom_fft (custom_fft)
_dft_cst_power -- 100 100 -- 0.07599 0.07726 -- <ipython-input-85-8502f1ddbe1f>:1:_dft_cst_power (_dft_cst_power)
<built-in...y.empty> -- 100 100 -- 0.00126 0.00126 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.empty> (<built-in method numpy.empty>)
<built-in m...ltins.len> -- 100 100 -- 0.00008 0.00008 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<method 'to...' objects> -- 100 100 -- 0.00025 0.00025 -- ~:0:<method 'tolist' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects> (<method 'tolist' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects>)
<method 'tr...' objects> -- 100 100 -- 0.00096 0.00096 -- ~:0:<method 'transpose' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects> (<method 'transpose' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects>)
<built-in m...py.arange> -- 100 100 -- 0.00109 0.00109 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.arange> (<built-in method numpy.arange>)
<built-in met...uiltins.len> -- 300 300 -- 0.00020 0.00020 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<built-in method builtins.len> -- 400 400 -- 0.00027 0.00027 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>)
Cooley–Tukey FFT algorithm#
See Cooley–Tukey FFT algorithm.
The FFT matrix is defined by the matrix computation
, then one coefficient is
(
):
Let’s assume K is even, then
.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(6, 3))
a = numpy.arange(0, 12) * (-2 * numpy.pi / 12)
X = numpy.vstack([numpy.cos(a), numpy.sin(a)]).T
ax.plot(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], 'o');
for i in range(0, 12):
ax.text(X[i, 0], X[i, 1], "exp(-2pi %d/12)" % i)
ax.set_title('unit roots');

Then:
Then:
Finally:
Now, what happen when K is odd, fallback to the original computation.
import functools
def cooley_fft_2p(x, fft_length):
cst = _dft_cst_power(x.shape[-1], fft_length, x.dtype)
return numpy.matmul(x, cst)
@functools.cache
def _build_fact(p2_2, fft_length, dtype):
first = numpy.exp(-2j * numpy.pi / fft_length)
fact = numpy.ones(p2_2, dtype=dtype)
for k in range(1, p2_2):
fact[k] = fact[k-1] * first
return fact.reshape((1, -1))
def build_fact(p2_2, fft_length, dtype):
return _build_fact(p2_2, fft_length, dtype)
def cooley_fft_recursive(x, fft_length):
if len(x.shape) != 2:
raise RuntimeError(
"Unexpected x.shape=%r." % (x.shape, ))
dtype = numpy.complex128 if x.dtype == numpy.float64 else numpy.complex64
if fft_length == 1:
return x[:, :1].astype(dtype)
if fft_length % 2 == 0:
def split(x):
even = x[:, ::2]
odd = x[:, 1::2]
return even, odd
def tmp1(even, odd, fft_length):
p2_2 = fft_length // 2
fft_even = cooley_fft_recursive(even, p2_2)
fft_odd = cooley_fft_recursive(odd, p2_2)
return fft_even, fft_odd, p2_2
def tmp2(x, fft_even, fft_odd, p2_2):
fact = build_fact(p2_2, fft_length, fft_even.dtype)
fact_odd = fft_odd * fact
return numpy.hstack([fft_even + fact_odd, fft_even - fact_odd])
# inplace
# result = numpy.empty((x.shape[0], fft_length), dtype=fft_even.dtype)
# numpy.multiply(fft_odd, fact, out=result[:, :p2_2])
# numpy.subtract(fft_even, result[:, :p2_2], out=result[:, p2_2:])
# numpy.add(fft_even, result[:, :p2_2], out=result[:, :p2_2])
# return result
even, odd = split(x)
fft_even, fft_odd, p2_2 = tmp1(even, odd, fft_length)
result = tmp2(x, fft_even, fft_odd, p2_2)
else:
result = cooley_fft_2p(x, fft_length)
return result
def cooley_fft(x, fft_length):
return cooley_fft_recursive(x, fft_length)
def custom_fft_cooley(x, fft_type, length, axis):
# https://github.com/numpy/numpy/blob/4adc87dff15a247e417d50f10cc4def8e1c17a03/numpy/fft/_pocketfft.py#L56
if fft_type == 'FFT':
if x.shape[axis] > length:
# fft_length > shape on the same axis
# the matrix is shortened
slices = [slice(None)] * len(x.shape)
slices[axis] = slice(0, length)
new_x = x[tuple(slices)]
elif x.shape[axis] == length:
new_x = x
else:
# other, the matrix is completed with zeros
shape = list(x.shape)
shape[axis] = length
slices = [slice(None)] * len(x.shape)
slices[axis] = slice(0, length)
zeros = numpy.zeros(tuple(shape), dtype=x.dtype)
index = [slice(0, i) for i in x.shape]
zeros[tuple(index)] = x
new_x = zeros
if axis == len(new_x.shape) - 1:
if len(new_x.shape) != 2:
xt = new_x.reshape((-1, new_x.shape[-1]))
else:
xt = new_x
res = cooley_fft(xt, length)
if len(new_x.shape) != 2:
res = res.reshape(new_x.shape[:-1] + (-1, ))
else:
perm = numpy.arange(len(x.shape)).tolist()
perm[axis], perm[-1] = perm[-1], perm[axis]
rest = new_x.transpose(perm)
shape = rest.shape[:-1]
rest = rest.reshape((-1, rest.shape[-1]))
res = cooley_fft(rest, length)
res = res.reshape(shape + (-1, )).transpose(perm)
perm[axis], perm[0] = perm[0], perm[axis]
return res
raise ValueError("Unexpected value for fft_type=%r." % fft_type)
def custom_fftn_cooley(x, fft_type, fft_length, axes):
if len(axes) != len(fft_length):
raise ValueError("Length mismatch axes=%r, fft_length=%r." % (
axes, fft_length))
if fft_type == 'FFT':
res = x
for i in range(len(fft_length) - 1, -1, -1):
length = fft_length[i]
axis = axes[i]
res = custom_fft_cooley(res, fft_type, length, axis)
return res
raise ValueError("Unexpected value for fft_type=%r." % fft_type)
shape = (4, )
fft_length = [3,]
axes = [0]
rnd = numpy.random.randn(*shape) + numpy.random.randn(*shape) * 1j
assert_almost_equal(custom_fftn_cooley(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes),
numpy_fftn(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes),
decimal=5)
%timeit -n 1 -r 1 test_fct(numpy_fftn, custom_fftn_cooley)
1.5 s ± 0 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 1 run, 1 loop each)
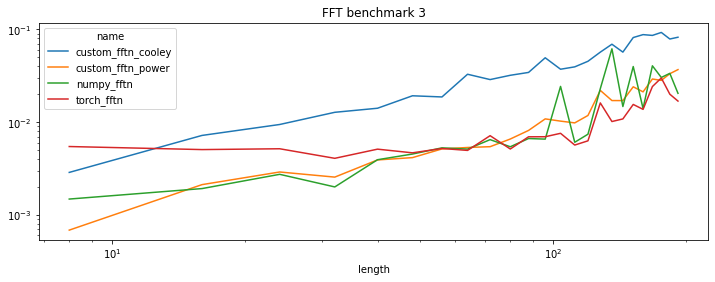
df = benchmark({
'numpy_fftn': numpy_fftn, 'torch_fftn': torch_fftn,
'custom_fftn_power': custom_fftn_power, 'custom_fftn_cooley': custom_fftn_cooley})
piv = df.pivot("length", "name", "average")
piv[:5]
100%|██████████| 24/24 [00:10<00:00, 2.35it/s]
| name | custom_fftn_cooley | custom_fftn_power | numpy_fftn | torch_fftn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| length | ||||
| 8 | 0.002873 | 0.000685 | 0.001482 | 0.005463 |
| 16 | 0.007197 | 0.002121 | 0.001922 | 0.005063 |
| 24 | 0.009443 | 0.002903 | 0.002739 | 0.005169 |
| 32 | 0.012783 | 0.002556 | 0.002003 | 0.004076 |
| 40 | 0.014142 | 0.003916 | 0.003937 | 0.005118 |
piv.plot(logy=True, logx=True, title="FFT benchmark 3", figsize=(12, 4));
df = benchmark({
'numpy_fftn': numpy_fftn, 'torch_fftn': torch_fftn,
'custom_fftn_power': custom_fftn_power, 'custom_fftn_cooley': custom_fftn_cooley},
power2=True)
piv = df.pivot("length", "name", "average")
piv[:5]
100%|██████████| 10/10 [00:11<00:00, 1.15s/it]
| name | custom_fftn_cooley | custom_fftn_power | numpy_fftn | torch_fftn |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| length | ||||
| 2 | 0.000575 | 0.000471 | 0.000722 | 0.019371 |
| 4 | 0.001153 | 0.000328 | 0.001130 | 0.018366 |
| 8 | 0.003678 | 0.000624 | 0.001779 | 0.019295 |
| 16 | 0.006843 | 0.002255 | 0.002192 | 0.020169 |
| 32 | 0.015574 | 0.003045 | 0.002736 | 0.017193 |
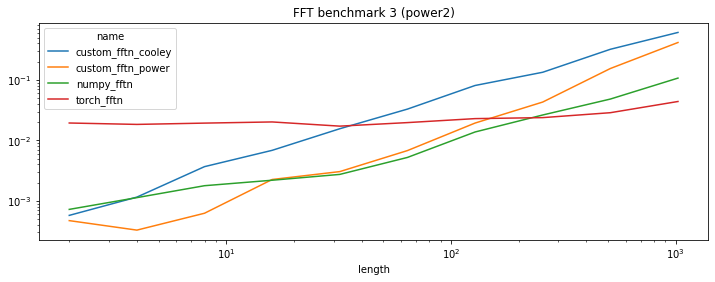
piv.plot(logy=True, logx=True, title="FFT benchmark 3 (power2)", figsize=(12, 4));
from pyquickhelper.pycode.profiling import profile2graph, profile
shape = [512, 256]
fft_length = [256]
axes = [1]
rnd = numpy.random.randn(*shape) + numpy.random.randn(*shape) * 1j
def f():
for i in range(100):
custom_fftn_cooley(rnd, 'FFT', fft_length, axes)
stat, text = profile(f)
gr = profile2graph(stat)
print(gr[0].to_text(fct_width=40))
cooley_fft_recursive -- 100 51100 -- 0.24497 2.68339 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:22:cooley_fft_recursive (cooley_fft_recursive)
split -- 25500 25500 -- 0.06264 0.06264 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:31:split (split)
tmp1 -- 100 25500 -- 0.09438 2.54540 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:36:tmp1 (tmp1)
cooley_fft_recursive -- 51000 200 -- 0.24336 2.54421 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:22:cooley_fft_recursive (cooley_fft_recursive) +++
tmp2 -- 25500 25500 -- 0.95948 2.04473 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:42:tmp2 (tmp2)
hstack -- 25500 25500 -- 0.04799 1.05776 -- <__array_function__ internals>:177:hstack (hstack)
_vhstack_dispatcher -- 25500 25500 -- 0.02712 0.07002 -- C:/Python395_x64/lib/site-packages/numpy/core/shape_base.py:218:_vhstack_dispatcher (_vhstack_dispatcher)
_arrays_for...dispatcher -- 25500 25500 -- 0.02361 0.04290 -- C:/Python395_x64/lib/site-packages/numpy/core/shape_base.py:207:_arrays_for_stack_dispatcher (_arrays_for_stack_dispatcher)
<built-in...hasattr> -- 25500 25500 -- 0.01929 0.01929 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.hasattr> (<built-in method builtins.hasattr>)
<built-in met...ay_function> -- 25500 25500 -- 0.03753 0.93975 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function> (<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function>) +++
build_fact -- 25500 25500 -- 0.02749 0.02749 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:18:build_fact (build_fact)
<built-in method builtins.len> -- 51100 51100 -- 0.01521 0.01521 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<method 'astype' ...darray' objects> -- 25600 25600 -- 0.22146 0.22146 -- ~:0:<method 'astype' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects> (<method 'astype' of 'numpy.ndarray' objects>)
f -- 1 1 -- 0.01449 2.70167 -- <ipython-input-144-55e663ef5e2e>:8:f (f)
custom_fftn_cooley -- 100 100 -- 0.00139 2.68718 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:112:custom_fftn_cooley (custom_fftn_cooley)
custom_fft_cooley -- 100 100 -- 0.00135 2.68568 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:69:custom_fft_cooley (custom_fft_cooley)
cooley_fft -- 100 100 -- 0.00082 2.68421 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:65:cooley_fft (cooley_fft)
cooley_fft_recursive -- 100 100 -- 0.00160 2.68339 -- <ipython-input-139-b9d3f22689f8>:22:cooley_fft_recursive (cooley_fft_recursive) +++
<built-in met...uiltins.len> -- 300 300 -- 0.00012 0.00012 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<built-in method builtins.len> -- 300 300 -- 0.00011 0.00011 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<built-in method builtins.len> -- 77200 77200 -- 0.02367 0.02367 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>)
<built-in method nu...nt_array_function> -- 25500 76500 -- 0.58675 0.93975 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function> (<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function>)
atleast_1d -- 25500 25500 -- 0.09562 0.13747 -- C:/Python395_x64/lib/site-packages/numpy/core/shape_base.py:23:atleast_1d (atleast_1d)
<method 'append...list' objects> -- 51000 51000 -- 0.01708 0.01708 -- ~:0:<method 'append' of 'list' objects> (<method 'append' of 'list' objects>)
<built-in method builtins.len> -- 25500 25500 -- 0.00822 0.00822 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.len> (<built-in method builtins.len>) +++
<built-in metho...py.asanyarray> -- 51000 51000 -- 0.01655 0.01655 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.asanyarray> (<built-in method numpy.asanyarray>)
hstack -- 25500 25500 -- 0.09871 0.90222 -- C:/Python395_x64/lib/site-packages/numpy/core/shape_base.py:285:hstack (hstack)
concatenate -- 25500 25500 -- 0.04882 0.57709 -- <__array_function__ internals>:177:concatenate (concatenate)
concatenate -- 25500 25500 -- 0.01049 0.01049 -- C:/Python395_x64/lib/site-packages/numpy/core/multiarray.py:148:concatenate (concatenate)
<built-in met...ay_function> -- 25500 25500 -- 0.51778 0.51778 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function> (<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function>) +++
atleast_1d -- 25500 25500 -- 0.04022 0.21751 -- <__array_function__ internals>:177:atleast_1d (atleast_1d)
_atleast_1d_dispatcher -- 25500 25500 -- 0.00838 0.00838 -- C:/Python395_x64/lib/site-packages/numpy/core/shape_base.py:19:_atleast_1d_dispatcher (_atleast_1d_dispatcher)
<built-in met...ay_function> -- 25500 25500 -- 0.03144 0.16891 -- ~:0:<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function> (<built-in method numpy.core._multiarray_umath.implement_array_function>) +++
<built-in metho...ns.isinstance> -- 25500 25500 -- 0.00892 0.00892 -- ~:0:<built-in method builtins.isinstance> (<built-in method builtins.isinstance>)